If y = f (x), the graph of y = af (x) is ), parallel to the xaxis Scale factor 1/a means that the "stretch" actually causes the graph to be squashed if a is a number greater than 1• The graph of f(x)=x2 is a graph that we know how to draw It's drawn on page 59 We can use this graph that we know and the chart above to draw f(x)2, f(x) 2, 2f(x), 1 2f(x), and f(x) Or to write the previous five functions without the name of the function f,Graph of f (½ x) = (½ x) 2 (This graph grows only half as fast as does the graph of the regular function, shown in the previous box) As you can see, multiplying inside the function (inside the argument of the function) causes the graph to get thinner or fatter
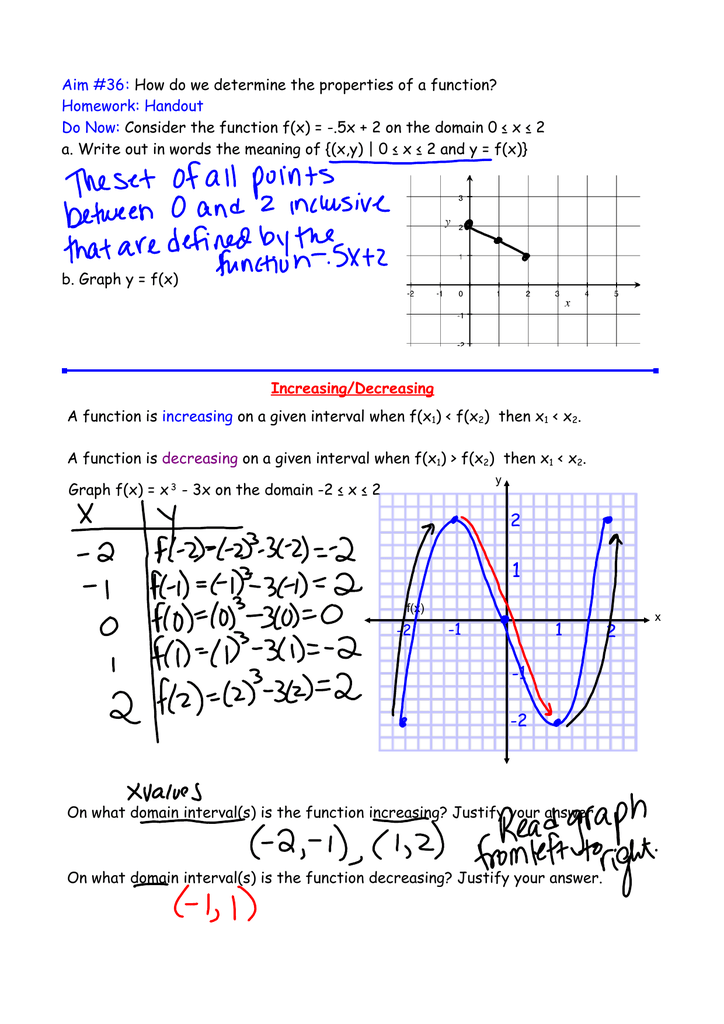
Aim 36 How Do We Determine The Properties Of A Function
What is f on a graph
What is f on a graph-Learning Objectives 451 Explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function's graph;E) If f'(x)=0, then the x value is a point of inflection for f To illustrate these principles, consider the following problems 1) Suppose a) On what interval is f increasing?
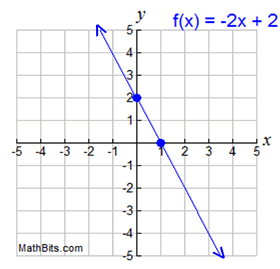



Features Of Function Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
Example 1 Fig 1 is the graph of the parabola f ( x) = x2 − 2 x − 3 = ( x 1) ( x − 3) The roots −1, 3 are the x intercepts Fig 2 is its reflection about the xaxis Every point that was above the x axis gets reflected to below the x axis And every point below the x axis gets reflected above the xDefining the Graph of a Function The graph of a function f is the set of all points in the plane of the form (x, f(x)) the graph of f to be the graph of the equation y = f(x) So, the graph of a function if a special case of the graphLinear functions have the form f(x) = ax b, where a and b are constants In Figure 111, we see examples of linear functions when a is positive, negative, and zero Note that if a > 0, the graph of the line rises as x increases In other words, f(x) = ax b is increasing on ( − ∞, ∞)
When x > 0, f(x) is equal to 2x When x = 0, f(x) is equal to 1 When x < 0, f(x) is equal to 2x When given a piecewise function graph, make sure to observe the given intervals where f(x) has varied graphs But before we try out examples that involve analyzing piecewise function graphs, let's go ahead and learn how we can evaluate and graph311 Recognize the meaning of the tangent to a curve at a point 312 Calculate the slope of a tangent line 313 Identify the derivative as the limit of a difference quotient 314 Calculate the derivative of a given function at a point The graphs of f (x) = 1 x f (x) = 1 x and y =Function Transformations Just like Transformations in Geometry, we can move and resize the graphs of functions Let us start with a function, in this case it is f
2) Sketch the graph of a function whose first and second derivatives are always X the inputs, factors or whatever is necessary to get the outcome (there can be more than one possible x) F the function or process that will take the inputs and make them into the desired outcome Simply put, the Y=f(x) equation calculates the dependent output of a process given different inputsFrom the graph of f ' (x), draw a graph of f(x) f ' is negative, then zero, then positive This means f will be decreasing for a bit, and will then turn around and increase We just don't know exactly where the graph of f(x) will be in relation to the yaxisWe can figure out the general shape of f, but f we could take the graph of f that we just made and shift it up or down along the y



Transformations Of Functions Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
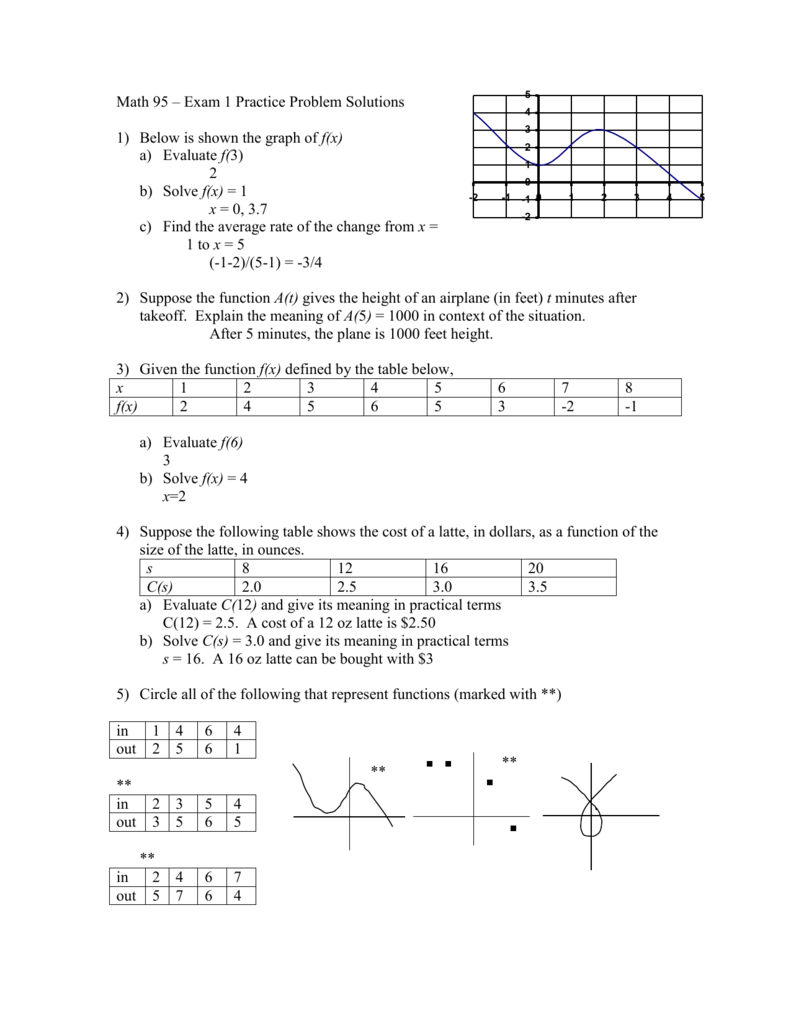



1 Below Is Shown The Graph Of F X
The derivative of a function y = f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to the change of the variable x It is called the derivative of f with respect to x If x and y are real numbers, and if the graph of f is plotted against x, derivative is the slope of this graph at each point Begin by evaluating for some values of the independent variable x Figure 251 Now plot the points and compare the graphs of the functions g and h to the basic graph of f(x) = x2, which is shown using a dashed grey curve below Figure 252 The function g shifts the basic graph down 3 units and the function h shifts the basic graph up 3 unitsIt means f(x) is always positive irrespective of the values of x Its graph is of v shape having sharp edge at origin



Graphs Of Functions




Lesson Explainer Even And Odd Functions Nagwa
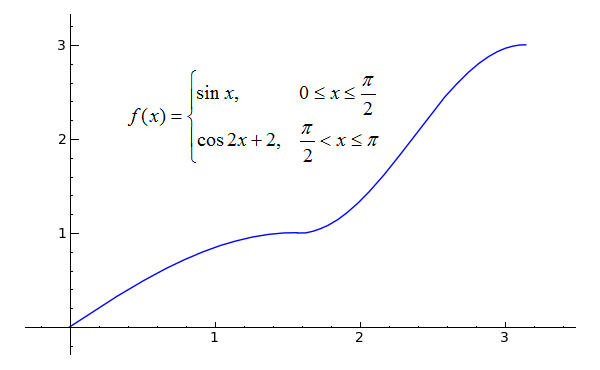
A math reflection flips a graph over the yaxis, and is of the form y = f (x) Other important transformations include vertical shifts, horizontal shifts and horizontal compression Let's talk about reflections Now recall how to reflect the graph y=f of x across the x axisUndefined derivatives Note From here on, whenever we say "the slope of the graph of f at x," we mean "the slope of the line tangent to the graph of f at x" In some cases, the derivative of a function f may fail to exist at certain points on the domain of f, or even not at allThat means at certain points, the slope of the graph of f is not welldefinedHence, the name "piecewise" function When I evaluate it at various x values, I have to be careful to plug the argument into the correct piece of the function



Continuous Functions An Approach To Calculus



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
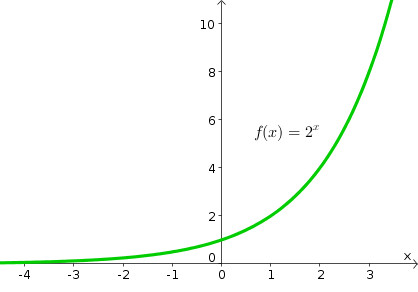
The graph always lies above the xaxis, but becomes arbitrarily close to it for large negative x;453 Use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the second derivative affects the shape of a function's graph;It remains to confirm f(x) and g(x) each share exactly one point in common with h(x) Again the tradition is to do so algebraically, but it might be instructive to look at some graphs of h(x) f(x) and h(x) g(x), such as the following Can we immediately generate graphs of other f(x), g(x), and h(x) satisfying the conditions of the problem?



What Does F X Mean Youtube



4 1 Probability Density Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Distribution Functions Cdfs For Continuous Random Variables Statistics Libretexts
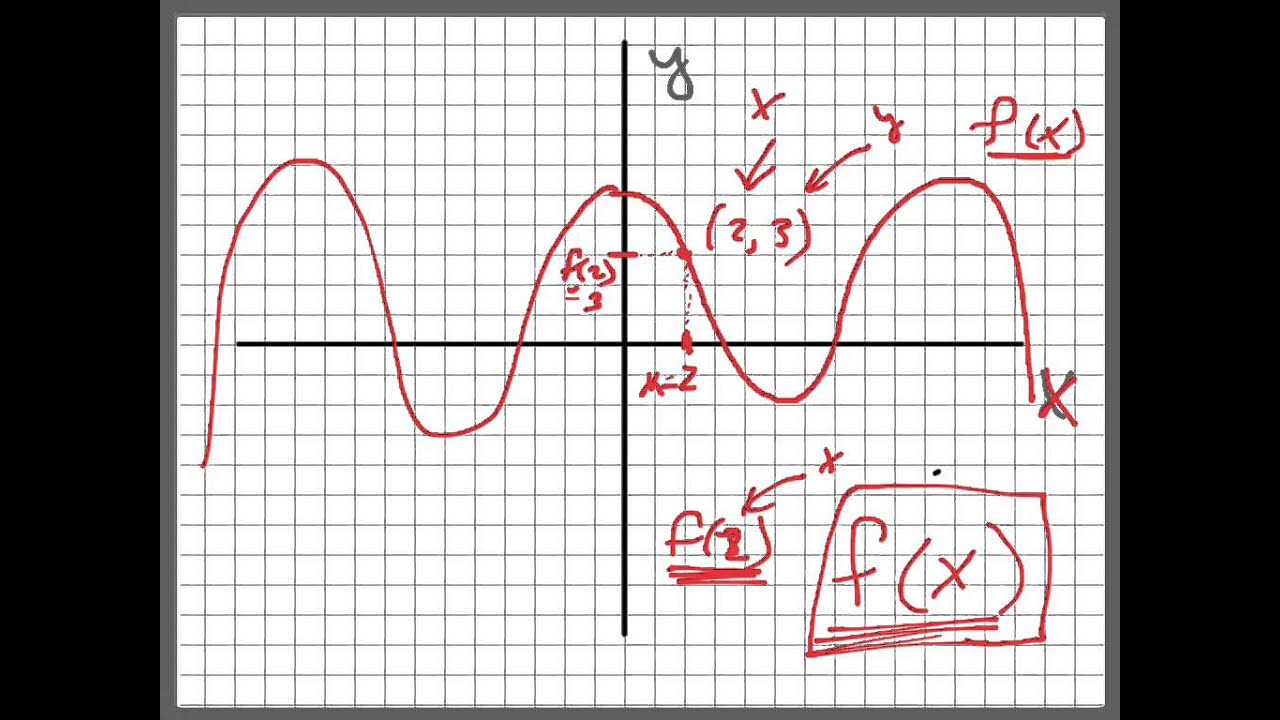
Algebra Graph f (x)=1 f (x) = 1 f (x) = 1 Rewrite the function as an equation454 Explain the concavity test for a function over an open intervalThis is the graph of y = f(x) First I want to label the coordinates of some points on the graph Since, for each point on the graph, the x and y coordinates are related by y = f(x), I can put the coordinates of these points in a list
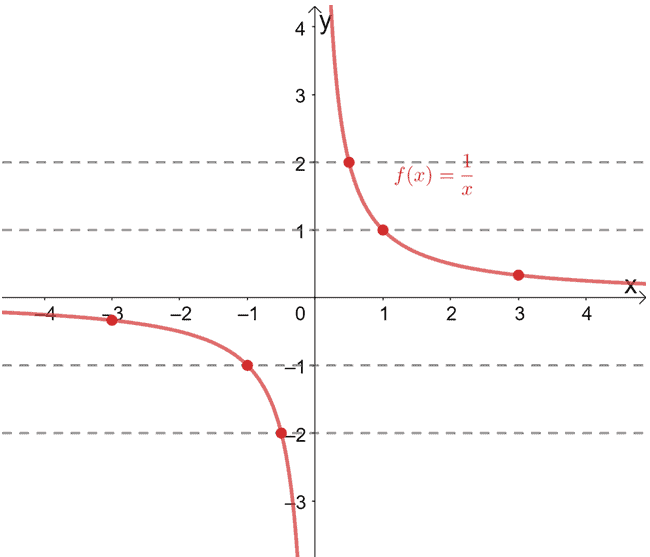



One To One Function Explanation Examples



Www Math Utah Edu Wortman 1050 Text If Pdf
This means that every x in f (x) must be replaced with g (x), which is equal to (2/x) Now f (x)=3/ (x2) which is equal to f (g (x))=3/ (2/x)2 This is f (g (x)) Please click on the image for a better understanding Next, we will simplify f (g (x))=3/ (2/x)2A graph is simply a drawing of the coordinate plane with points plotted on it These points all have coordinates (x, y)In the graph of a function, the ycoordinate has the value f (x), meaning the coordinates of the graph of a function are (x, f (x))The possible values of x are elements of the domain of the function, and the possible values for f (x), or y, are the elements of the range ofBy $f(x) = x^2 4$ I am telling you that if you input a number $x$ to this function then the function squares $x,$ subtracts 4 and returns the result Thus for example if $x = 3$ then $y = f(3) = 3^2 4 = 9 4 = 5$ To graph this function I would start by choosing some values of $x$ and since I get to choose I would select values that make the arithmetic easy



Graphs Of Functions




4 2 The Mean Value Theorem Mathematics Libretexts
We know that a continuous function is integrable over a closed bounded domain In fact if f(x,y,z)=1 on the domain D, then you certainly know that the tripleBased on the definition of vertical shift, the graph of y 1 (x) should look like the graph of f (x), shifted down 8 units Take a look at the graphs of f ( x ) and y 1 ( x ) The graphical representation of function (2), g ( x ), is a line with a slope of 4 and a y intercept at (0, 1)On what interval is f decreasing?




Derivative And Tangent Line




How To Find Domain And Range From A Graph Video Khan Academy
452 State the first derivative test for critical points;Since the sine graph is made by rotating around a unit circle, it cycles every time the full circle is complete Which of the answer choices makes a graph identical to that of fThus, the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote The equation d d x e x = e x {\displaystyle {\tfrac {d}{dx}}e^{x}=e^{x}} means that the slope of the tangent to the graph at each point is equal to its y coordinate at that point




The Exponential Function Math Insight



Operations On Functions Stretches And Shrinks Sparknotes
Definition for Y = f(X) Y=f(x) is a concept regarding the setup of a formula used to perform analysis during problemsolving efforts Let's look at how Y=F(x) works within the problemsolving process, the benefits of Y=F(x), as well as some frequently asked questionsEven functions If $f(x)$ is an even function, then for every $x$ and $x$ in the domain of $f$, $f(x) = f(x)$ Graphically, this means that the function is symmetric with respect to the $y$axis Thus, reflections across the $y$axis do not affect the function's appearanceB) Does f have a maximum or minimum value?
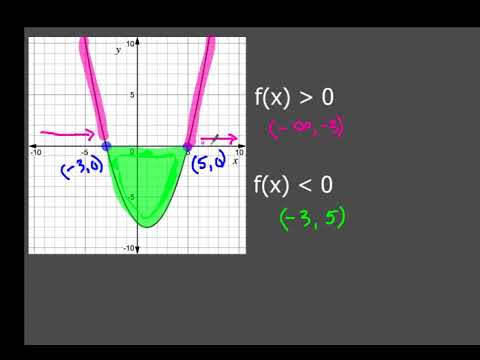



How To Tell Where F X Is Less Than 0 Or Greater Than 0 Youtube



Sage Calculus Tutorial Differentiability
You get these gems as you gain rep from other members for making good contributions and giving helpful advice #6 Report 15 years ago #6 (Original post by gordon02) 'function of x' f (x) basically means y, and f' (x) means dy/dx The x can have a value, so for example, f (x) = 2x 1, then f (1) = 3Graph f(x) = −2x 2 3x – 3 a = −2, so the graph will open down and be thinner than f(x) = x 2 c = −3, so it will move to intercept the yaxis at (0, −3) Before making a table of values, look at the values of a and c to get a general idea of what the graph should look likeF ( x h) − f ( x) in such a way that we can divide it by h To sum up The derivative is a function a rule that assigns to each value of x the slope of the tangent line at the point ( x, f ( x )) on the graph of f ( x ) It is the rate of change of f ( x) at that point



What Does F X Mean Youtube



The Exponential Function Math Insight
Given the function f (x) as defined above, evaluate the function at the following values x = –1, x = 3, and x = 1 This function comes in pieces;F(x) P Q x 0 x 0 x y Figure 1 A graph with secant and tangent lines A secant line is a line that joins two points on a curve If the two points are close enough together, the slope of the secant line is close to the slope of the curve We want to find the slope of the tangent line m — which equals theAlgebra Graph f (x)=x Find the absolute value vertex In this case, the vertex for is Tap for more steps To find the coordinate of the vertex, set the inside of the absolute value equal to In this case, Replace the variable with in the expression The absolute value is the distance between a number and zero



Probability Density Function
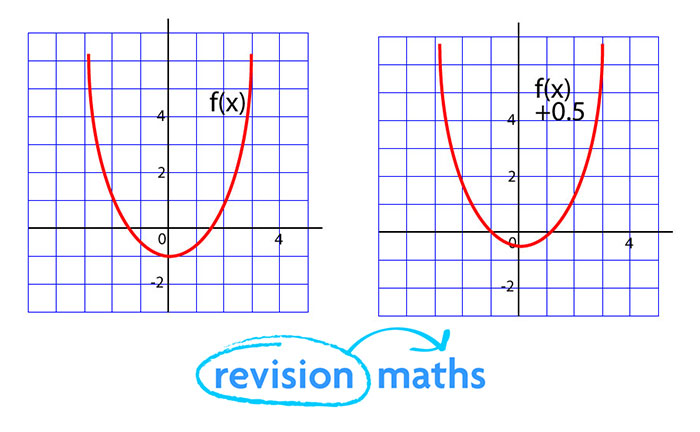



Functions Maths Gcse Revision
Graph of Cubic Polynomials f (x) = x³4x Geometrical Meaning of Zeros Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting yourFind domain and range from graphs Another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs Because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x axis The range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y axisThe graph of the function is the set of all points (x,y) (x, y) in the plane that satisfies the equation y= f (x) y = f (x)



Fx Graph




Features Of Function Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
F (x) = x is interpreted as the function of x equals x For instance y=x is a function of x where each value y is equal to x along its range In fact y=x is a line that increases left to right and is 45 degrees from the horizontal 3K views
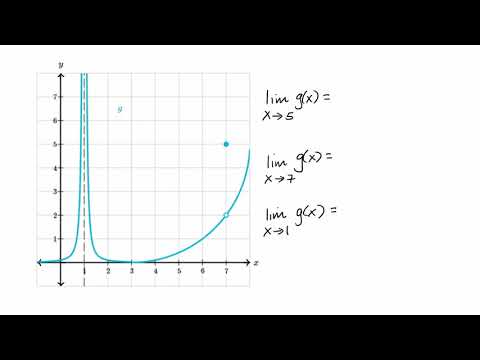



Estimating Limit Values From Graphs Video Khan Academy
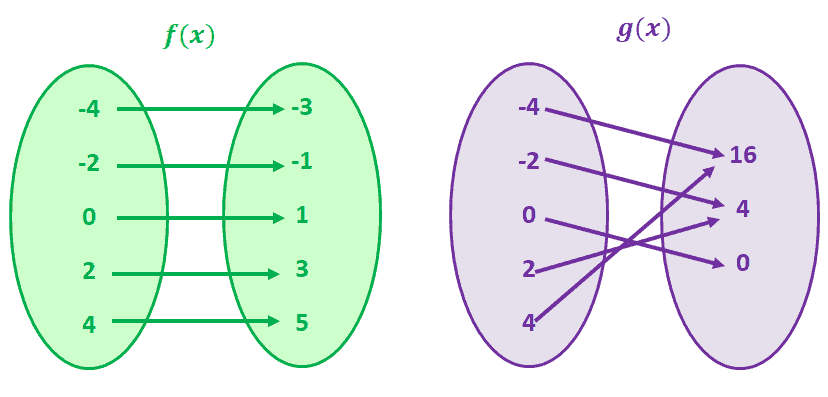



One To One Function Explanation Examples



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations
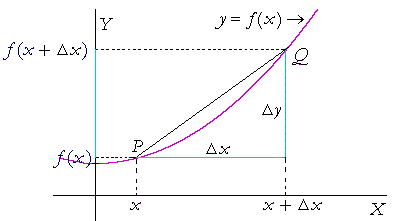



The Meaning Of The Derivative An Approach To Calculus



Horizontal Line Test For Function To Have Inverse Expii



Increasing And Decreasing Functions




Efofex Software




Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica




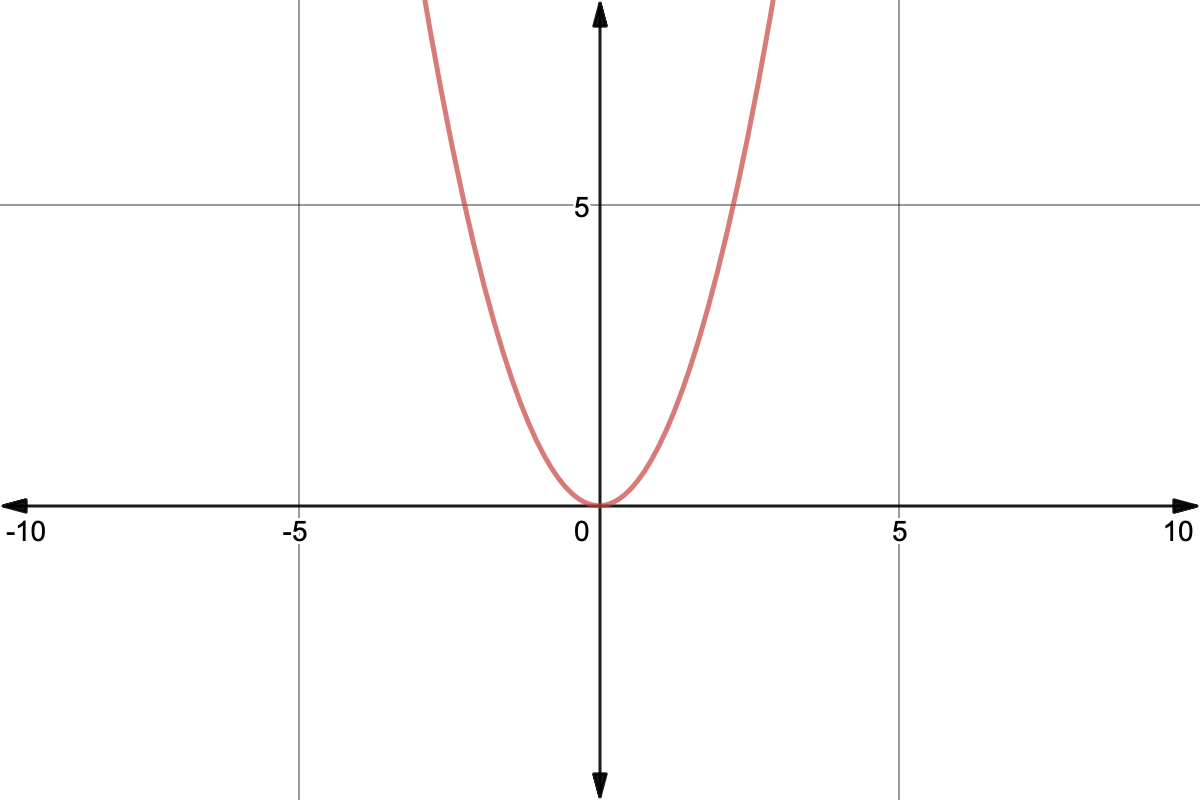
The Graph Of F X Ax 2 All Quadratic Functions Have Graphs Similar To Y X 2 Such Curves Are Called Parabolas They Are U Shaped And Symmetric With Ppt Download



Average Value Of A Function




What Does F X Mean Youtube



What Does F X X Mean Quora
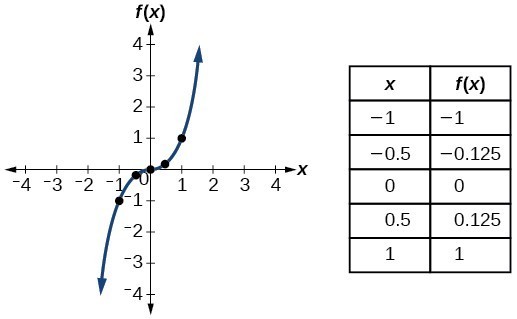



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra




Graphing The Basic Functions
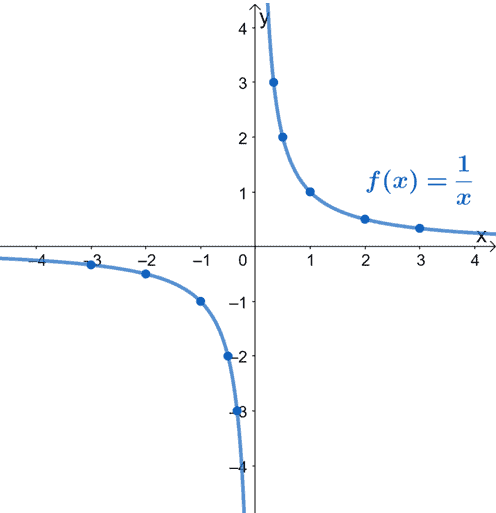



Reciprocal Function Properties Graph And Examples




What Is The Difference Between Y F X And Y F X Quora
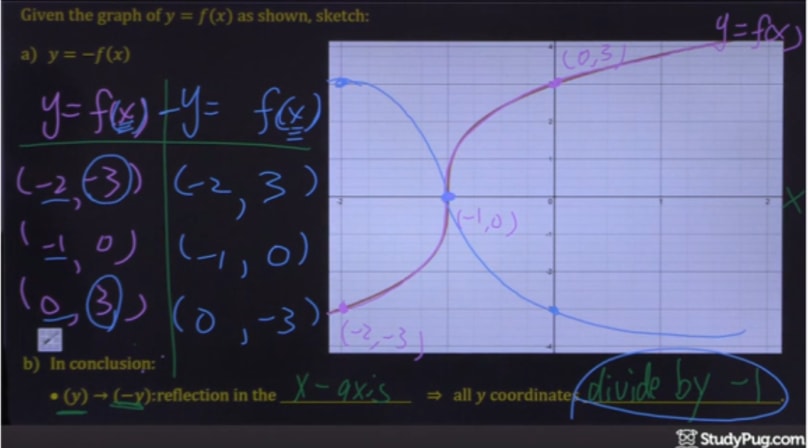



How To Reflect A Graph Through The X Axis Studypug



Inverse Functions



Operations On Functions Stretches And Shrinks Sparknotes



Operations On Functions Reflections And Rotations Sparknotes




Inverse Function Wikipedia



1




Maths What Is A Function Y F X Youtube




Increasing And Decreasing Functions




Transformations Of The 1 X Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




What Is A Power Function Definition Equations Graphs Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Aim 36 How Do We Determine The Properties Of A Function



All Elementary Mathematics Study Guide Principles Of Analysis Derivative Geometrical And Mechanical Meanings Of Derivative




5 3 Inverse Functions Mathematics Libretexts



Graph Of A Function Wikipedia



Function Graph Types
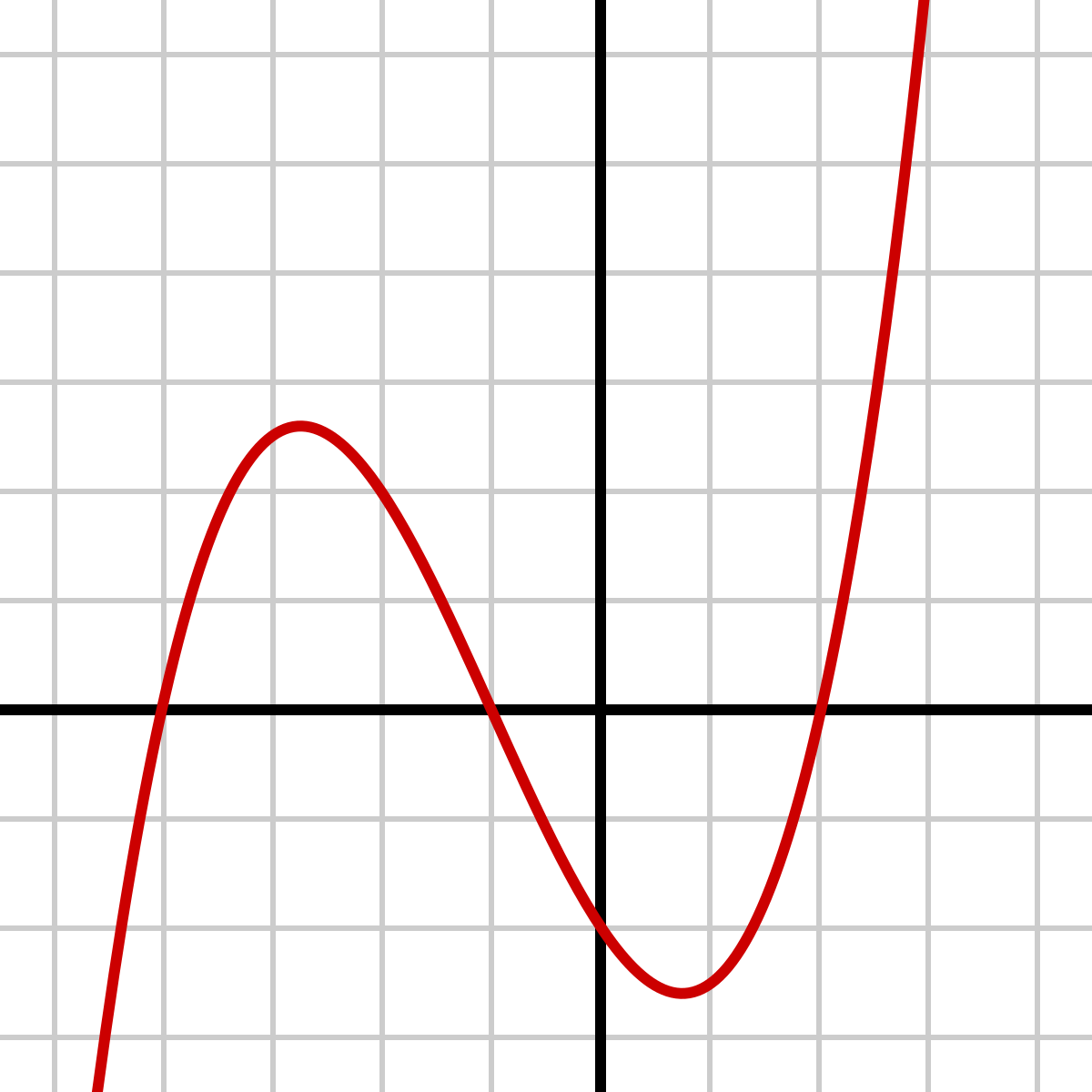



Polynomial Wikipedia
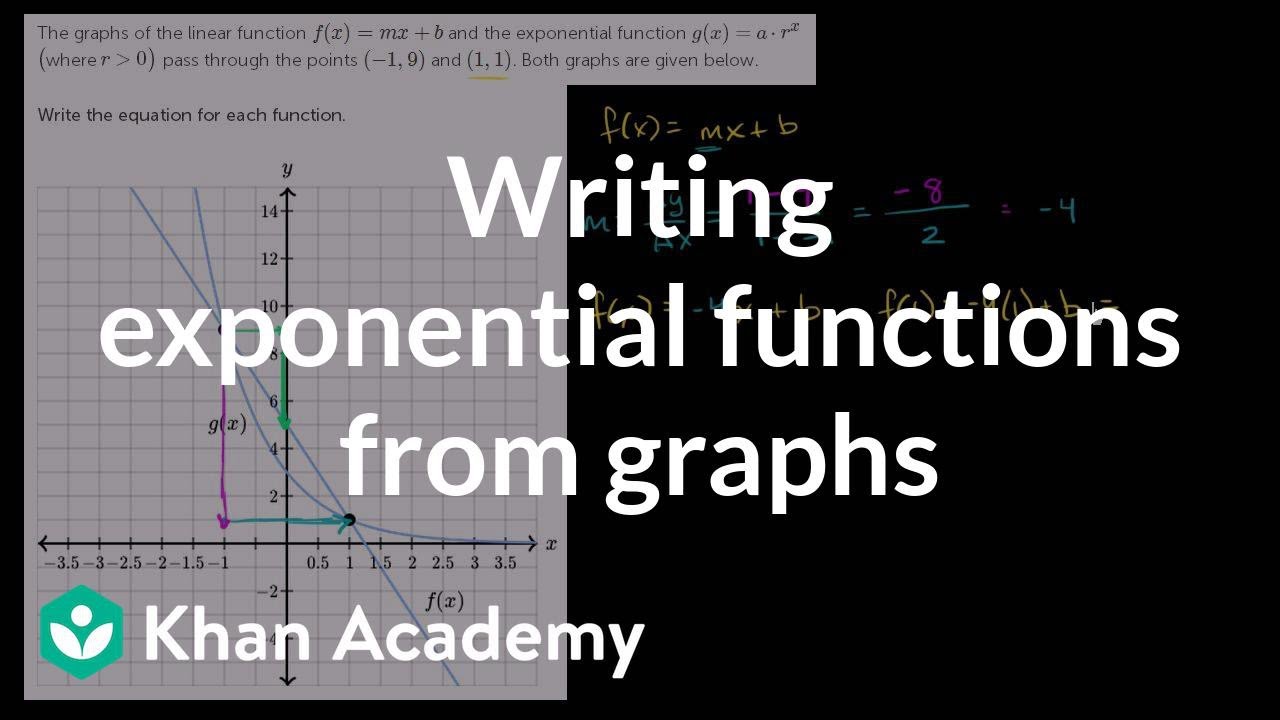



Writing Exponential Functions From Graphs Algebra Video Khan Academy



Introduction To Exponential Functions




Continuity At A Point Video Khan Academy




Shifting And Stretching Graphs The Math Doctors
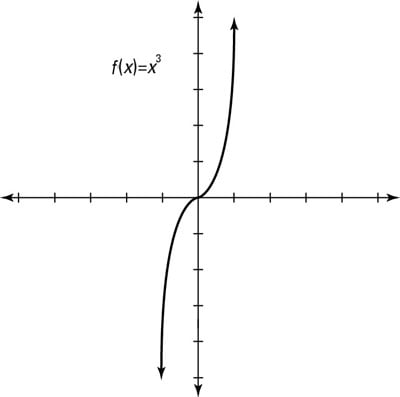



How To Identify Even And Odd Functions And Their Graphs Dummies



Derivatives And Integrals




What Is A Power Function Definition Equations Graphs Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Search Q Parent Functions Tbm Isch




Common Functions Reference



1




How To Find The Range Of A Function Video Khan Academy
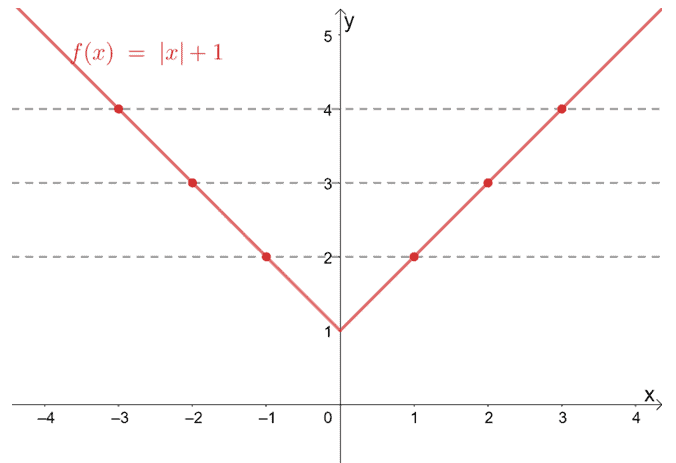



One To One Function Explanation Examples




Lesson Explainer Even And Odd Functions Nagwa
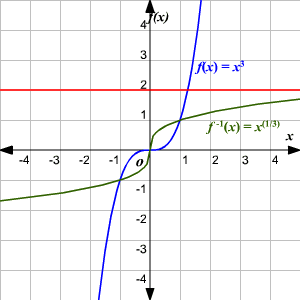



One To One Functions



Discontinuous Functions
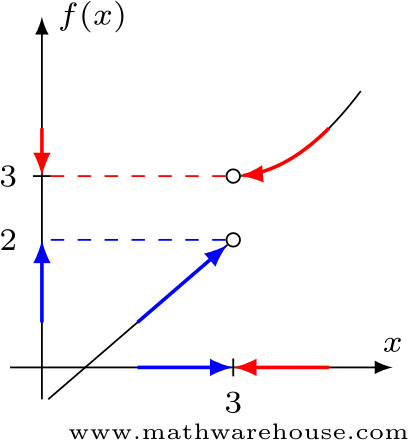



When Limits Don T Exist How To Determine The 4 Reasons That Limits Fail Either The Limit




Mini Math Lessons Fx 9860gii Graphs Of Functions And Their Derivatives Calculus Blog Strategies Resources Edtech Tips



Reflections Of A Graph Topics In Precalculus
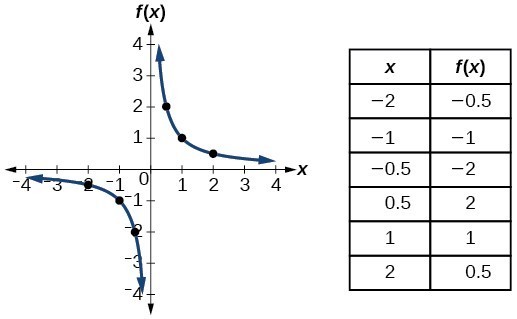



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra




3 7 Derivatives Of Inverse Functions Mathematics Libretexts
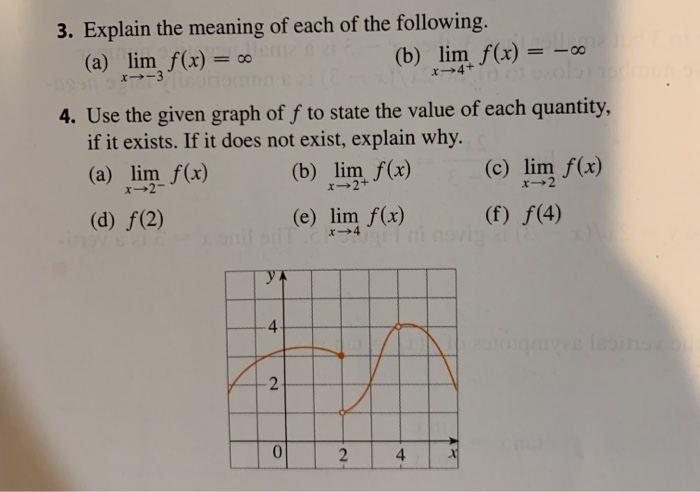



3 Explain The Meaning Of Each Of The Following A Chegg Com
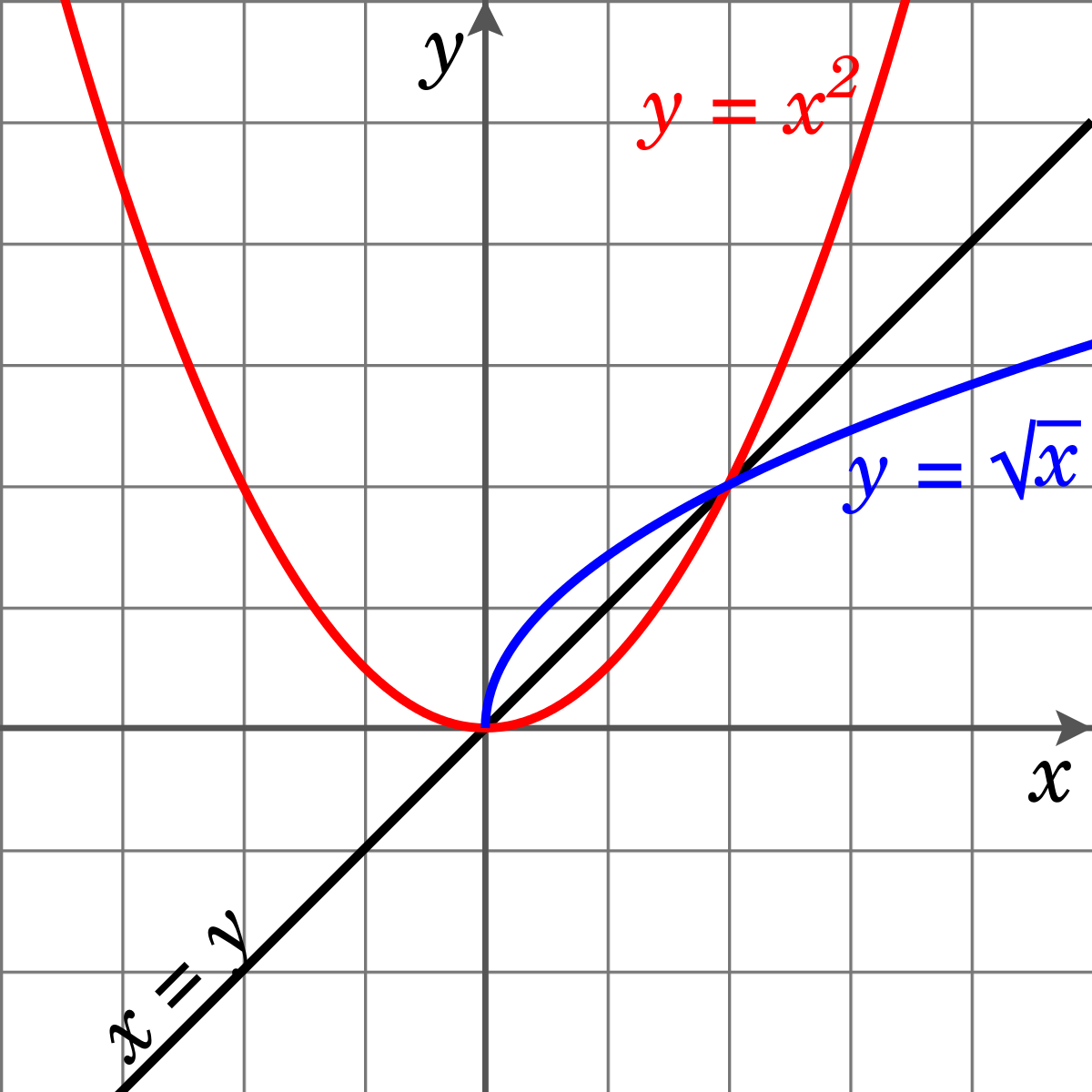



Restriction Mathematics Wikipedia




E Mathematical Constant Wikipedia



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



Understanding F X Function And How To Graph A Simple Function Math Algebra Graphing Functions F If 7 F If 4 Showme
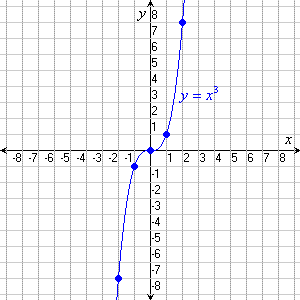



Cubic Functions



Graphs Of Functions




Domain Range And Codomain
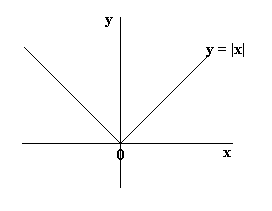



Functions Algebra Mathematics A Level Revision
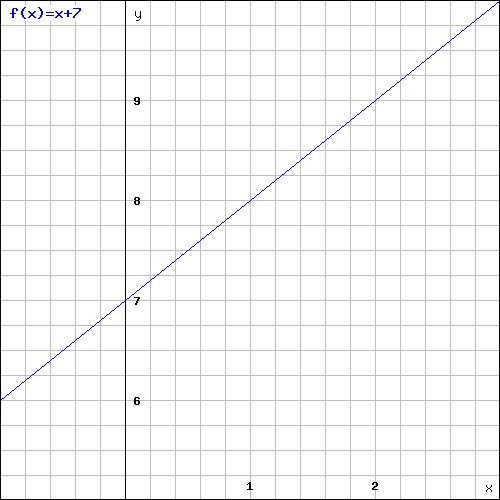



Functions And Linear Equations Algebra 2 How To Graph Functions And Linear Equations Mathplanet



What Is The Difference Between Y F X And Y F X Quora



Transformations Of Functions Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
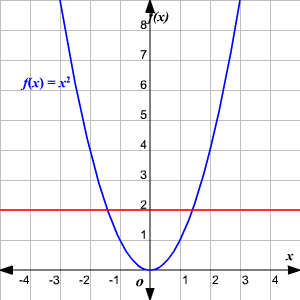



One To One Functions
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Four_Types_of_Forex_FX_Trend_Indicators_Nov_2020-01-df673b5bd0764b14bc7a6b2b6d53bb55.jpg)



Four Types Of Forex Fx Trend Indicators



Operations On Functions Translations Sparknotes




Function Rules Based On Graphs Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation
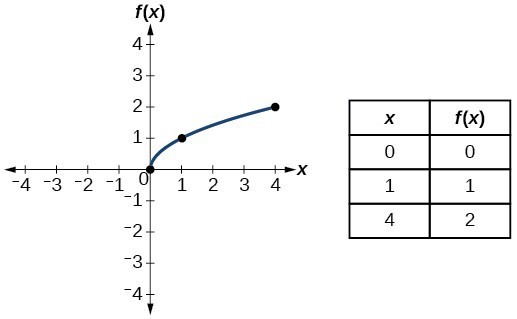



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra




What Is The Difference Between Y F X And Y F X Quora
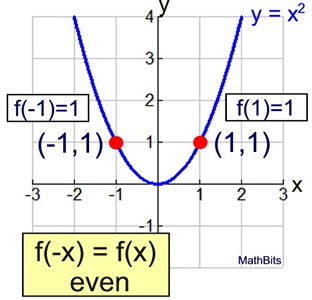



Odd And Even Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math



Graphs Of Functions



Domain And Range Of A Function




Transformations Of The 1 X Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Higher Maths Revision Notes Goodbye Functions And Graphs



Sharetechnote




Function Transformations
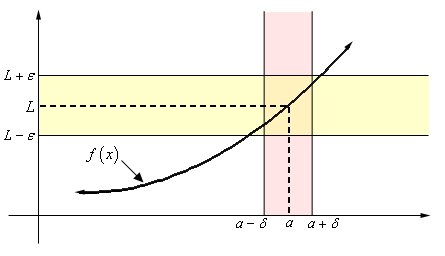



Calculus I The Definition Of The Limit



Calculus The Definition Of The Derivative



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations



No comments:
Post a Comment